It is always difficult to evaluate the ROI of a technology, because it is the way you use it that generates (or not) a Return on Investment. It is not your Customer Data Platform, by itself, that will generate euros. It is your ability to implement ROIst uses. So talking about ROI means talking about CDP use cases.
We will see that there are two types of ROI-generating use cases:
- Those that save time, to be more productive (because time is money, saving time is saving money).
- Those that increase marketing performance.
At the end of the article, we will also talk about the costs of a CDP. It is difficult to talk about Return on Investment without talking about investment at some point. ROI is the benefits compared to the costs incurred. If your CDP earns you 100,000 euros, but costs you twice that amount, there is no ROI.
We therefore offer you a complete overview of the subject of the ROI of CDPs. Enjoy your reading!
📕 Contents
Estimating the ROI of your CDP: the summary table
To justify a CDP project, you need to be able to justify the ROI to management. We saw in the introduction that there are two types of use cases, those that reduce costs (automation of low value-added tasks, optimisation of advertising costs thanks to better targeting, etc.) and those that provide performance incentives (better retention, upsell/cross-sell, increase in the average basket, better campaign conversions, etc.).
Time savings can be in marketing or tech tasks. To evaluate what this represents financially speaking, to estimate the ROI generated, it must be measured in Full Time Equivalent (FTE). Marketing performance increments are measured in euros.
The way to measure the ROI of a CDP project is to define the different benefits that the technology will deliver. These benefits are in fact what are called use cases. You must then assess for each benefit or use case a realistic business impact. To give you an idea, here is a table listing benefits and their estimated business impact. It is this kind of table, and the process involved in its construction, that will help you to estimate the ROI of your CDP as closely as possible.
| Categorie | CDP profit | Estimated performance increments |
|---|---|---|
| Performance of marketing actions | Améliorer la qualité de vos données en réduisant le temps nécessaire à leur exploitation | - 5% bounce rate on my email campaigns |
| Performance of marketing actions | Campagnes multicanal cohérentes (Ads et email par exemple) en termes de messages et de timing | Increased reach by 50% and purchase intent by 20% on both my Ads and email campaigns |
| Performance of marketing actions | Pousser des recommandations produits personnalisées lors du parcours d'achat du client | 5% increase in the average basket |
| Performance of marketing actions | Identifier les profils inactifs et mettre en place des campagnes spécifiques | 5% churn reduction |
| Performance of marketing actions | Utiliser le retargeting pour les campagnes d’abandon de panier | 10% reduction in my abandoned cart rate |
| Productivity gains - Data integration | Réduire le temps dédié aux intégrations (maintenance et développement) | 60%+ reduction in FTEs for data engineers |
| Productivity gains - Data integration | Rendre les marketers autonomes dans la création de segments et et d'audiences | 50% reduction in time spent going back and forth between data and marketing teams |
| Elimination of unnecessary costs | Stopper les campagnes payantes sur des clients/utilisateurs existants | 20% reduction of the Ads / SEA budget |
| Risk management and compliance | Suivre et contrôler les destination où les données sont envoyées ainsi que la manière dont elles sont collectées et stockées. | Removal of any risk of non-compliance with regulations (GDPR) and associated potential fines |
We will now describe in detail each of the main families of benefits offered by a CDP:
- Marketing performance. A CDP increases the performance of marketing actions.
- Operational performance. A CDP enables productivity to be increased and operational costs to be reduced.
- Risk management. A CDP allows for better governance of customer data…and therefore reduces the risk of non-compliance with the RGPD.
- Strategic value. Having a CDP is a competitive advantage. It allows you to better exploit customer data and gain market share against competitors who are not equipped with this technology.
- *Do you really know what a CDP is?
This page is dedicated to CDP. If you are reading this, you are probably familiar with the term, but do you really know what a CDP is? If you are unsure, check out our definition of CDP.
ROI & Marketing Performance
Companies that implement a CDP have this benefit in mind: increased marketing performance. The unification of customer data in a CDP and dynamic segmentation (among other things) allow for better targeting of campaigns and marketing actions in general. This optimised targeting results in lower costs and higher conversion rates.
The qualitative leap in terms of customer experience also makes it possible to increase KPIs such as the average basket, churn, reach, click and conversion rates, etc. The logic is simple: better exploited customer data > personalisation and targeting of marketing actions > optimised performance.
McKinsey has shown in a study that personalisation can multiply ROI of marketing expenses by 5-8 times. Better connection and interconnection of data, their unification in a CDP, greater accessibility and better control of the data offered are necessary (but not necessarily sufficient) conditions for effective personalisation.
How can we concretely evaluate the impact of a CDP on marketing performance? In our opinion, there are 3 criteria to take into account:
Velocity
Personalisation data loses value over time. It is subject to the cruel principle of entropy. For this reason, customer segments must be updated regularly. A customer who belongs to segment A may well belong to segment B the next day, the next hour, depending on the events they perform.
Personalisation data evolves rapidly over time, so it must be constantly updated to maintain its value. Without it, marketing targeting becomes less accurate and relevant.
Part of the marketing performance increment of a CDP is its ability to update personalisation data in real time, for example through dynamic segmentation. The more scalable your data, the higher the ROI your CDP is likely to deliver.
Scaling marketing actions
CDPs enable omnichannel customer dialogue, orchestrating messages across all advertising and marketing channels. Several studies have shown that cross-channel campaigns deliver better performance than single-channel campaigns. For example, one study showed that companies that coordinated Facebook and email campaigns increased campaign reach by 77% and sales by 22% on customers who were targeted by both campaigns.
With a CDP, you can deploy cross-channel campaigns. You just have to decide what kind of campaigns you want to deploy and estimate the performance increments.
Personalization & context
Personalizing your messages is one thing, being able to adapt them to a global and unified customer context is another. Let’s take a concrete example. As a retailer, you sell online and you also have a few shops where you make physical sales.
Without a unified customer view, your data is siloed: when you calculate your LTV in order to identify your best customers, you may be in for a nasty surprise. A very good online customer who is not really a customer because they return many items to the shop. Your marketing efforts to sell more to this supposed VIP customer are in vain.
We’ve talked about this before. A CDP allows you to personalise and contextualise marketing and advertising messages by taking into account all customer data. Thanks to the 360° customer view, you can more easily detect the best time, the best channel and the best offers and content to propose.
ROI & Operational Performance
This category of “operational performance” refers to all the costs that a PSC allows you to save. Doing as much, or even more and better, with less: that is the goal. The cost savings come from the automation capabilities of CDPs. This of course depends on the CDP you choose and how you implement it. Automation is possible at 3 levels:
Data integration
Data preparation is often time consuming. If you are using marketing software, you should know this. Before activating the data, you have to spend a lot of time integrating it into the tools. And this integration work has to be done as many times as you have tools. Companies have between 10 and 20 tools. Do the math…
A CDP makes it easier to connect the different data sources and unify the data. Customer Data Platforms offer a whole battery of native connectors that save precious time in data integration. You save tens and even hundreds of hours (of your engineers). What used to take weeks can now take days… That’s a huge benefit of CDPs.
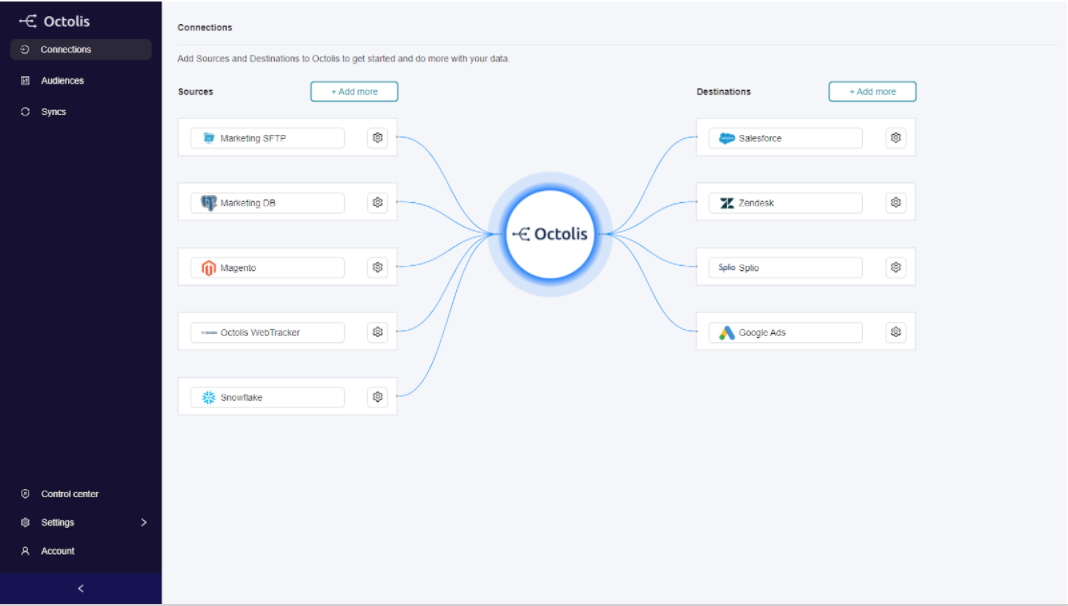
In a CDP, data integration is facilitated by connectors. Example: Octolis.
How many integrations do you need to maintain? How many new tools do you intend to deploy within 2 years? Ask yourself these questions and calculate the costs you will save if you use a CDP.
Marketing Ops & Data teams
Without CDP, a marketing team that wants to create a segment has to go through several steps: define the target segment (“individuals who have purchased 2 products in the last month”), have the data engineers calculate the segment and finally integrate the segment into the various marketing tools. The same process must be repeated to create new segments, check that the segments are up to date or when new tools are added to the marketing stack.
This constant back and forth between the data team and the marketing team makes everything complicated, time consuming and therefore expensive. Customer journey analysis, data cleansing, aggregate creation: without a CDP, the data team is the marketing team’s go-to person. They are constantly being called upon.
With a CDP, the marketing team gains autonomy and can carry out simple preparations of customer data without having to knock on the data team’s door. This saves bandwidth for the data/tech team. This is also why a CDP is synonymous with operational efficiency.
Optimisation of media budgets
The targeting of media campaigns is a guarantee of both effectiveness and profitability. That’s why marketers all agree that targeting is best practice. Targeting a campaign makes it possible to match the offers proposed with the needs of each client. Targeting a campaign also allows you to send messages only to customers who are likely to be interested.
You replace quantity (mass emailings) with quality: it is quantity that determines the cost of campaigns. For example, the number of impressions of your advertising campaigns. By targeting, you save money! In order to assess the ROI of your CDP, try to estimate the cost savings that would result from better targeting of your campaigns.
ROI & Risk Management
Risk Management covers several areas. Here, we want to focus on one specific risk: the one related to the General Data Protection Regulation, the so-called GDPR. The GDPR requires companies to comply with strict rules regarding the security of personal data and the respect of privacy. Customers’ personal data must be stored securely. But when data is spread across dozens of tools, data governance becomes a nightmare! A CDP makes it possible to centralise the management of customer data and its governance, and to manage access rights in a detailed manner.
Data governance will become a key issue in the years to come. A CDP makes it possible to properly manage the risk of non-compliance with the RGPD – a risk that can materialise in the form of a fine of up to 20 million dollars or 4% of the company’s global turnover. That’s a lot of money! Estimate the financial risk you face in the absence of RGPD compliance. Consider that your CDP will allow you to control this risk: this is an element to be taken into account when evaluating the ROI of CDPs.
- Different types of CDP
There are three main types of Customer Data Platforms: CDP data management, CDP analytics and CDP engagement. To find out more, read our page “Types of CDP” .
ROI & Strategic Value
So far, we have mainly talked about the benefits of a CDP in the short to medium term: better marketing performance, better operational performance, risk management. But a CDP also offers long-term benefits which, by definition, are more complex to measure. We are talking about the competitive advantages that a company with CDP has.
The idea is simple: using a CDP enables a much richer and more personalised customer experience. In the long run, this translates into awareness, reputation, brand preference and ultimately gains in market share. But also higher margins. You meet customer expectations that your competitors cannot manage, your customers are willing to pay the price.
The most successful companies are those that deliver the best customer experiences. CDPs are the technology family that allows you to leverage your customer data and take the customer experience to the next level.
When deploying a CDP, you also need to take that long-term view. Many companies focus on initiatives that generate short-term results: quick wins. In reality, much of the value and benefits of CDP will be realised in the future. It is necessary to combine the short/medium term vision with the long term vision, the tactical approach with the strategic approach.
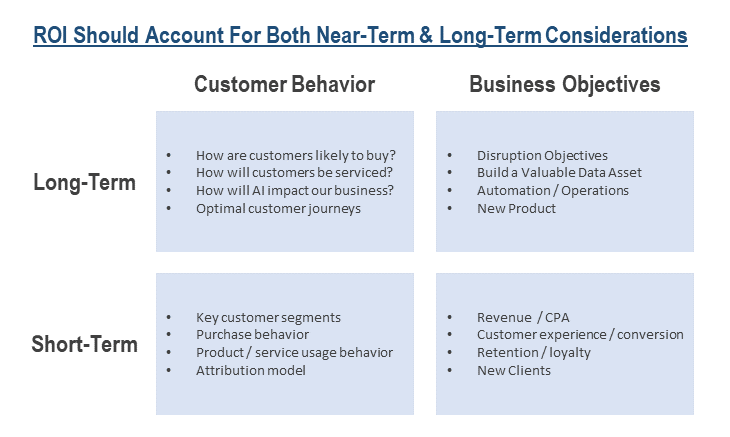
Source : CDP Institute.
What is the cost of a CDP?
As we said in the introduction, measuring the Return on Investment means comparing the benefits and costs of the project. If we want to talk about the ROI of CDPs seriously, we need to talk about the benefits (which we have just done) but also the costs. Here is a table summarising the costs of a CDP project:
| PME / ETI | Grande entreprise | |
|---|---|---|
| Software license | 20 to 60k€ / year | 70 to 200k€ / year |
| Setting up | 10 to 40k€ | 40 to 200k€ |
| Operation & Development | 5 to 20k€ / year | 30 to 100k€ / year |
We have talked a lot about the benefits of your CDP. We will go faster on the costs, not because it is less important but because we have published a page entirely devoted to this subject. You will find the link to it a few lines below.
There are three cost items to consider:
- The cost of the CDP software, i.e. the cost of the licence. The main variable used to set the price of the platform is the number of contacts, but others may intervene: number of events, number of CDP users, level of support, number of activated modules, etc. A CDP costs between 20 and 200 k€ per year. The positioning of the CDP (mid-market vs. large companies), the level of support and the age of the publisher are the 3 main factors explaining this large price difference.
- The cost of implementing the software within the company**. The deployment of a CDP takes between 2 and 4 months. It includes several stages: specification of target use cases, data mapping, specification of the data model and flows, configuration of import flows, configuration of the CDP, etc. The level of support provided by publishers varies greatly. In general, consulting firms and integrators are involved in the management and execution of the deployment. You should plan on a budget ranging from 10 to 200 k€.
- The cost of operating your CDP: the maintenance and evolution of your tool. You will certainly have to deploy new use cases, connect new data sources, evolve the data model and train new staff. It is estimated that a budget for operation and upgrades of between 20 and 30% of the cost of the software is required. It is possible, under certain conditions, to reduce this expense item, as we explain in our page dedicated to the cost of CDPs.
- *Cost of a CDP
To explore the subject in more detail, we invite you to read our page: How much does a Customer Data Platform cost?.


